A test in software development world is a piece of code written to verify that the code works as expected. An ideal test validates these 3 areas:
- Does the code solve the problem it was designed to solve?
- Does the code respond correctly to inputs? Both valid and invalid inputs
- Does the code perform optimally and reliably.
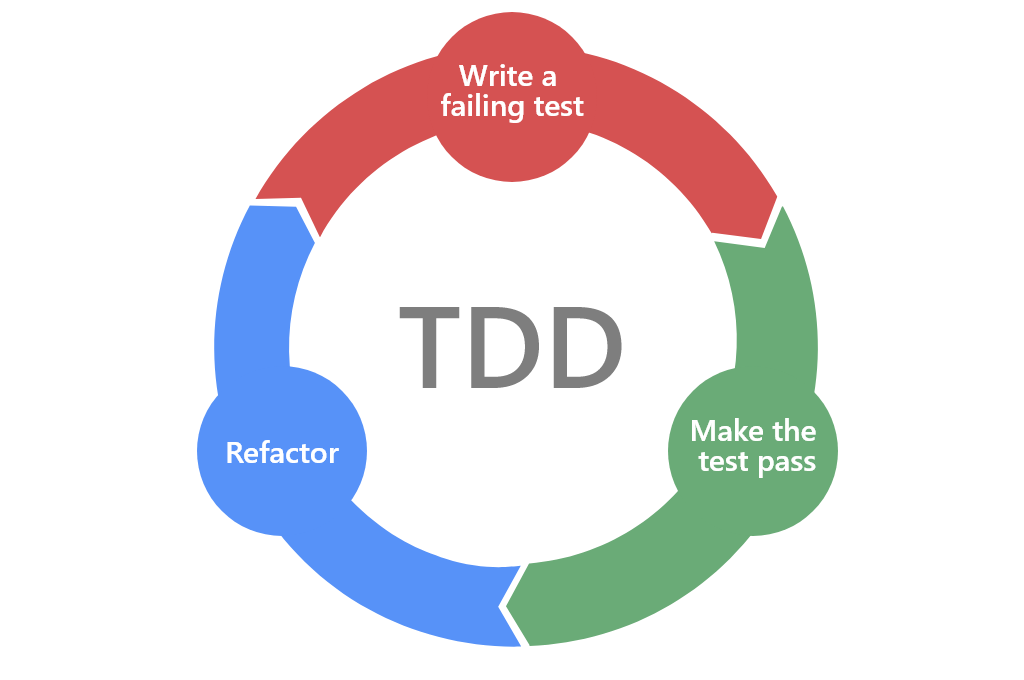
Image Credits: Chris Ried, marsner.com
What is TDD?
Test Driven Development (TDD) is a software development approach where the requirements are transformed into specific test cases and then code is written to satisfy these tests; we would typically write just enough code for the tests to pass; and then refactor the working code for better optimisation; nothing more.
Red-Green-Refactor: Tests are written first, these tests fail (Red) then we write code that makes the tests pass (Green) Then we Refactor the working code
Why should you care?
I am sure you’re already very familiar with manual testing, your manual workflow will be similar to this scenario; open up a page, fill the form with proper data and verify that the data is submitted(Happy path). Open up the form again but this time around supply bad data, could be text in a number field and verify that it fails successfully(Unhappy path). Imagine what happens as the app grows 😔
You see the need for automated testing?
Some of the benefits of TDD include:
- It is a required skill for most good jobs
- TDD helps with regressions so previously working functionality is not broken by new enhancements
- It helps verify the requirements developed
- It encourages a design first mentality for development
- It prevents over engineering as we’re only doing bare minimum
- Leads to fast delivery cycles
- It builds developer confidence with releases
- It encourages a customer centric design
- It ensures reduced maintenance cost
- It boosts confidence when refactoring and improving code — this is the biggest for me
- Writing tests also expose code smells, this one becomes valuable with time
There’s a post on different types of testing here
Testing approaches
- Black box testing: we assume we have no access about what happens on the inside but only validate the outputs from the system
- White box testing
Testing tools and frameworks
- SUnit frameworks eg JUnit for Java, NUnit for dotNet
- UI frameworks eg Selenium
- System frameworks eg Chaos monkey, Simian Army
Concepts
- Tests
- Test suites
- Before and after hooks
- Assert: used to tell the test the expected output
- Test runner — synchronous vs asynchronous
Strategies and techniques for testing
- Dependency Injection: in this strategy, the object is passed with the required dependency.
- Test doubles: test doubles are pretend objects. The two major ones are stubs and mocks; we also have fakes and spies.
- Best practices
Tests shouldn’t worry about implementation details
Limitations of TDD
- TDD is not a magic-wand; it doesn’t always prevent bugs just like bugs get past compilation. If you have a bug in the test code and implementation code, it can go undetected, hence, you need to understand the problem you are solving.
- TDD can seem slower at the beginning because you need to think about the interfaces, write the tests before implementing code to make these tests pass.
- One of the strongest arguments against TDD is that test need to be maintained when requirements change; you’ll need to change the tests and then implement code that makes this new tests pass.
Comments